The unstoppable combination of technological change and the rapid development of consumer demands and expectations is transforming the global economy. The borders that delimited the business and industrial sectors are disappearing, and technology allows customers to align with new types of companies to cause disruptive changes in existing business models: from Uber to loans between individuals.
We are in the age of digital platforms, which are open 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, for a new generation of consumers who expect to have almost instantaneous services. These platforms are found in all customer-facing operations, from financial services and health to travel and tourism.
Today we all know that the largest businesses in the world are those whose activity is based on platforms which have managed to build their own business model. It is no coincidence that the 5 largest companies in the world are Google, Amazon, Apple, Facebook and Microsoft, which have managed to create a digital ecosystem through which they interact directly with users.

Nowadays, platforms and ecosystems are two critical instruments of digital transformation. As such, we see how they transcend sectors such as health, for example. Where users who use mobile devices, want to send an email safely to their doctor, consult the results of medical tests or analysis, process medical prescriptions and request appointments online. But nevertheless; Nowadays the companies do not finish here, they look for generate alliances with other consolidated platforms to solve logistical questions (Amazon), for example.
Financial services also face large disruptive phenomena. And here also open opportunities for new business models. In this way there has been a shift from conventional banking to mobile applications. In this sense, it may be that banking as we know it is no longer relevant. But financial intermediation will remain relevant anywhere in the world, the question is, what will be the best way to offer this to customers?
The future of e-commerce platforms
The business model as a platform has been confirmed by startups such as Uber and AirBnB, where several investors and other companies have invested millions of dollars before the potential of the firms. Between both they add a stock market value of about $ 98 Billion Dollars (USD).
Today the consumer is omnichannel and nobody escapes this trend. This can be seen reflected in the searches with intent to buy in the countries, which are increasingly made from a mobile phone. In other continents this trend is more, however; in Latin America consumers buy more online, for ease, convenience and greater product offer. The main benefit of e-commerce platforms is to be in constant contact with the customer, listen to them, understand them and accompany them throughout the shopping experience.

Characteristics of the Platforms
The digital platforms to which we are giving increasing use have characteristic elements that are of enormous interest from a social and economic point of view, namely:
Power Crowd: The platforms visualize a greater capacity of citizens to organize and interact globally with fewer barriers than other systems. We are talking not only about accessing or offering services and objects, but also that citizens collaborate with a social or political objective. With disintermediation, new organizational structures and connectivity, the power of citizens has been reinforced. YouTube, TaskRabbit and Etsy are some exemplary cases.
Disintermediation: Digital platforms provide the power that makes it easier for people to eliminate commercial intermediation. In the value chain, the reduction of agents is sought to access a service, information or a good without diminishing the value of what is offered.
The citizen producer: Linked to this power crowd, we find the figure of the producer citizen, decentralized economic agent and not organized into a business structure that can use the platforms as a provider of goods and services. An economic figure that thanks to the platforms is amplified and consolidated as a viable life model.
Trust and reputation: One of the greatest assets that the user of digital platforms can achieve is a good reputation to generate the necessary trust so that the network that structures a platform can bring activity and demand. The interesting thing is that this reputation is not only of the one that provides but also of the one that receives, which generates dynamics of collaboration and good behavior that even exceed what legal requirements may involve in terms of protecting consumers and users. From the platforms that initially incorporated reputation and evaluation systems such as eBay or Amazon, we have moved to systems with highly efficient and transparent evaluation and reputation operations. Companies like AirBnB, Booking.com are continually innovating to make the “feedback” provided by users achieve the best user experience.
In this way the citizen can access new service platforms, request loans, insurance or generate new information with added credentials and of enormous value.
Where are we going? What is the trend
The trend is to promote business models in this area is a sign of potential growth to achieve viable business. Which also implies the opportunity to attract financing by private and public investors.
The investment side is also being complemented with acquisitions of platforms by traditional companies, for example, Marriott is associated with a coworking company to market unused spaces in its hotels; Peugeot has integrated Koolicar to provide shared car services; Ikea bought TaskRabbit to cover the services part of microtareas; or Avis bought Lyft and Zipcar.
We must bear in mind that the platforms we know now will be subject to disruption thanks to the innovation that allows a distributed technology such as the blockchain, in some cases we will find that they will not belong to a specific company but to users or digital cooperatives. Situation that can revert the leadership in the market of some platforms and that has already begun to be visualized in some cases as shown by this graph of recognized platforms in the market and its competitors based on blockchain technology, such as:
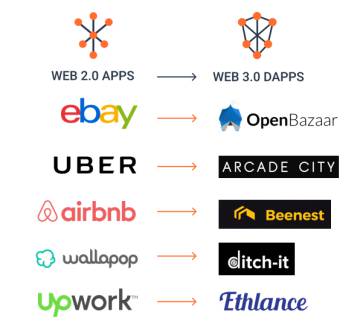 Does this work in practice? In this article, you will observe some projects that lead us towards a decentralized collaborative economy.
Does this work in practice? In this article, you will observe some projects that lead us towards a decentralized collaborative economy.OpenBazaar. eBay without eBay in between. “A free online market. No platform commissions. Without restrictions. Earn cryptocurrencies” can be read on their website. Buy and sell freely. One year ago they received $ 5 million of investment and announced their intention to issue their own token later.
Arcade City. Uber without Uber in between. Arcade City technology allows building a global network of local drivers’ cooperatives called guilds. The guild leaders work together to provide a reliable service in their local area. They started in Austin (Texas) and there are already guilds in Rio de Janeiro, London, Villahermosa (México), Taipei (Taiwan) and Los Baños (Philippines).
These are not the only ones. Beenest, AirBnB without AirBnB in between; Ethlance, UpWork without UpWork in between; DitchIt; Wallapop without Wallapop in between … Most of them are less mature projects than OpenBazaar or Arcade City but they allow us to anticipate a very interesting and decentralized future.
Iomob. It is a startup that is working with fintech mass aggregation services. Startup of Spanish capital that combines open source and blockchain technology to decentralize mobility, leading the Internet of Mobility (mobility) revolution in smart and sustainable cities.
WOULD YOU LIKE TO SHARE ANY COMMENT?
