In today’s marketplace, where existing companies are competing with disruptive new players such as: AirBnB, UBER, Facebook, Alibaba, Amazon, etc … These new companies take over the essential market of existing organizations and threaten with radically modifying the functioning of that market.
Traditional or incumbent companies face a choice: do they stay true to their old model, risking obsolescence, or adopt the new disruptive business model to compete?
We are familiar with cases where low-cost airlines such as Ryanair and EasyJet redefined customer expectations and turned the market around. Conventional airlines, such as British Airways, Delta Airlines, in order to compete, were also forced to introduce low-cost offers, which meant adopting a radically different business model. But, for British Airways and Delta, this did not work.
If we take Delta Airlines as a case for analysis, we could affirm that it operated under a traditional airline model and diversified towards an unrelated low cost airline model with Delta Song, which turned out to be fundamentally different from the traditional model, which created logics of inconsistent business within the company and increased the risk that the director would interfere ineffectively. As an example, headquarters managers were unable to allow Delta Song to make their own decisions regarding scheduling and pricing, adapting them to the demands of their low-cost business model. The new model failed, and Delta Airlines had to part with its low-cost airline.
So as companies adopt disruptive ways to operate in order to compete in rapidly changing markets, knowing how to manage multiple models in parallel may be what differentiates organizations that will have problems from those that will succeed.
It should be borne in mind that technology has become a potential transforming element that is already applied to optimize processes, automate services, make the meeting between supply and demand more efficient or eliminate intermediaries, and that promises many more benefits in the coming years. years, causing disruptive innovation.

Business models
Emerging technologies such as: Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, robotics, Blockchain, UAV (unmanned aerial vehicles) and virtual and augmented reality have given way to new business models that are changing the economy, our expectations and our behaviour. This process responds to a clear dynamic, to a structure that has occurred throughout all the technological waves and that follows a process that begins with: (1) a scientific advance, (2) that materializes in a new technology, (3) that reaches the business world, (4) and changes the economic and / or social organization.
There are a wide variety of disruptive business models that are emerging, but due to their relevance and impact, I prefer to point out the 4 most important ones below: a) Those derived from the digital transformation of companies b) the platform economy model c) The decentralized model and d) the pop-up economy and superfluous markets.
Digital transformation causes the generation of new business models
The digital transformation of companies is one of the great current issues. Based on the breadth that digital transformation provides, we would say that it paves the way and gives companies the opportunity to innovate and introduce new business models to corporations.
Although the businesses affected by this digitization are still being determined, what is clear is that companies must face a change in strategy, and must transfer resources to new digital initiatives, redesign the organization and transform their culture if they do not want to stay. behind. In this way, they will be able to take advantage of the value creation opportunity that disruptive innovation represents, instead of seeing it as a threat.
In this section I always like to mention the success story that Domino’s Pizza has had in digital transformation. This huge company, with more than 15,000 establishments spread around the world, can boast of being leaders in Pizza Delivery around the world. The formula for its success lies in the improvement of its products based on the opinions of its customers through social networks as the main source of information. Together with the digital adaptation they have made (orders can be placed from any device: smartphone, smart TV, smartwatch … So much so that half of their orders are online).
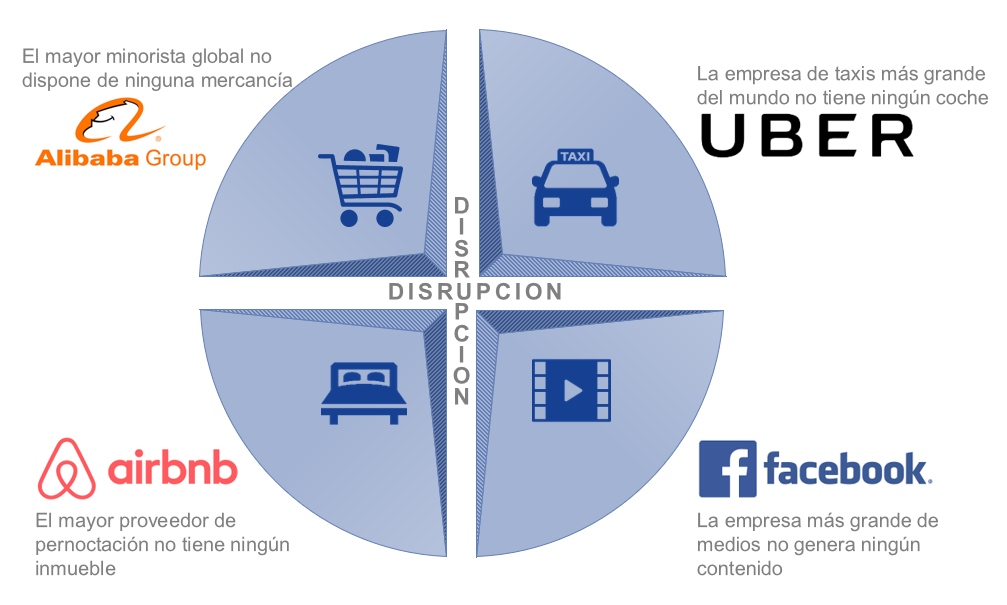
Collaborative economy platforms
In this sense, we look at the P2P (person-to-person) business models, or the collaborative economy. They are new business models based on platforms or apps that operate on demand and that normally digitize an activity that was already done analogically, whether for profit or not. They eliminate the intermediary company from the equation, which is replaced by the platform that facilitates the connection with the person who provides the service or has the property to be acquired.
This new model allows to take advantage of underused resources; they put new products and services on the market; they facilitate the best supply and demand option; accelerate innovation; they create demand and new activity, and they stimulate the market. In addition, it offers a reduction in prices or in a better quality and variety of services, also of those provided by traditional actors. The success cases in this type of platform are: AirBnB or UBER, alluding to the negative externalities associated with these in matters of competition, regulation, taxes.
Decentralized model
Consumers no longer need an intermediary entity that centralizes the provision of goods and services, but can do it directly between them, through platforms.
One of the great niches of the P2P model is crowdfunding, which facilitates financial contributions between peers. There are different types: donation; reward (the person who contributes receives compensation that the beneficiary establishes); equity crowdfunding (investment) or crowdlending (loans).
These models are already part of the fintech revolution that threatens the banking sector. They disintermediate the process and decentralize it, without the need for financial entities in between (although they do need a platform). The technology used in a high percentage in this type of financial business mentioned is Blockchain. As we know; Bitcoin is a digital currency that uses cryptographic encryption as a security and anti-counterfeiting system. It is the first of its kind that can operate without the need for banks or a central authority, without revealing data on the identity of those who carry out the transactions.
Superfluid markets model
Technological development has made it possible to create a StartUp in one day, to set up an internet sales store in a few hours.
Everything in less time, cheaper and extraordinarily easier than a decade ago. Technology is creating new superfluid markets (very agile, without resistance or friction and near zero transaction costs) and transforming companies and markets as we knew them.
Ease of information and decision-making, networking and automation, robotics, and new manufacturing modes are changing entire industries and sectors. Modifying products and services at an increasingly rapid speed.
It is necessary to point out that these types of companies use the cloud to host their business, they use Open Source programs for their management and electronic commerce and payment platforms to carry out their transactions over the Internet.

Conclusions
From a business perspective, the impact of disruptive business models is clear: Financial, insurance, transportation, automobile, hotel or aerospace industries and sectors are besieged by new StartUps that threaten their business and accelerate inevitable change. . However, to what extent are these a threat? Don’t historical operators have better defenses?
Experts believe that the outlook is more favorable for large companies, which do not stop growing. This is the case, for example, with the case of the hotel industry, which projects a future of continuous success. However, hoteliers are facing a necessary renovation and transformation of which they are often aware and in which they are taking part. Some choose to innovate and others lobby to impose what can be seen as barriers to entry to new business models.
Another debate that arises around the substitution of intermediary companies for platforms and about the disintermediation that technologies like Blockchain facilitate is how a disintermediated market is perceived that is organized directly between consumers and suppliers, without the need for a central authority.
Of course, technology already allows it, but the system often paralyzes and is an obstacle to its application. An example of this are the cases of UBER and AirBnB in Spain, where their activity has been limited by law. The competition authorities of both the European Union and Latin America raise their voices in this regard, that they do not put barriers to entry for these new actors and legislators are asked to guarantee the right to technological innovation, even if it represents a I challenge the traditional way of doing business, especially considering that new technologies can improve efficiency in favor of consumers. One point in favor of this type of model is that they have trust mechanisms based on digital reputation systems that allow for scoring, evaluating and commenting on the services used or goods provided and the people with whom the transactions are carried out.
In this way, the way we relate and how we consume is transformed. The trust of the service becomes somewhat more measurable through the reputation that is valued through the internet.
DO YOU WANT TO SHARE YOUR IDEAS WITH US?
